Para importar una lista de waypoints con el servidor Webserver, los datos deben estar ordenados en archivos de texto separados, cifrados en UTF8 para soportar caracteres especiales.
Pueden usar su aplicación favorita de hojas de cálculo o convertir los waypoints desde otra base de datos para que concuerde con la estructura descripta abajo.
Recomendamos fuertemente que se cree primero un waypoint personalizado en Air Nav Pro y que se lo descargue desde el sitio Web para obtener la estructura de archivo correcta. De este modo, no es necesario tipear los nombres de las columnas manualmente (lo que podría causar errores de tipeo y/o mala estructura que podría no ser reconocida como un archivo válido de importación).
Estructura de archivos de waypoints
Para ser un archivo de waypoint válido, debe empezar con una hilera que enumere los nombres de las columnas, separadas por un carácter de tabulación (tecla TAB). Las otras líneas representan los valores de los waypoints (una línea por waypoint). Los valores pueden estar vacíos, pero deben estar separados por un carácter de tabulación.
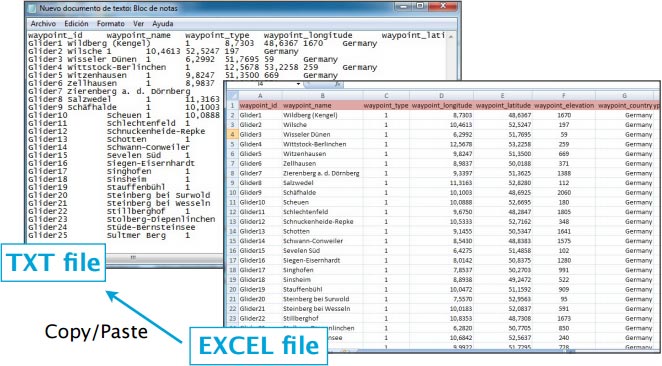
Lo más sencillo sería utilizar el MS Excel para trabajar sobre la estructura y luego copiarla y pegarla en un archivo TXT del conocido «Notepad» (Bloc de Notas):
Los nombres de las columnas y sus definiciones son:
- waypoint_id (texto corto, identificación del waypoint)
- waypoint_name (texto, corta descripción del waypoint)
- waypoint_type (número: 1=Aeropuerto, 2=punto VFR, 3=Waypoint, 4=Helipuerto,
5=pista de agua, 8=punto IFR, 10=DME, 11=NDB, 12=VOR, 13=NDB/DME, 14=VOR/ DME, 15=TACAN, 16=VORTAC)
- waypoint_longitude (número con decimal)
- waypoint_latitude (número con decimal)
- waypoint_elevation (número, elevación en pies)
- waypoint_country (texto)
- waypoint_state (texto, ejemplo California)
- waypoint_channel (texto)
- waypoint_frequency (número, sólo para radio ayudas)
- main_runway_orientation (número del 1 al 360)
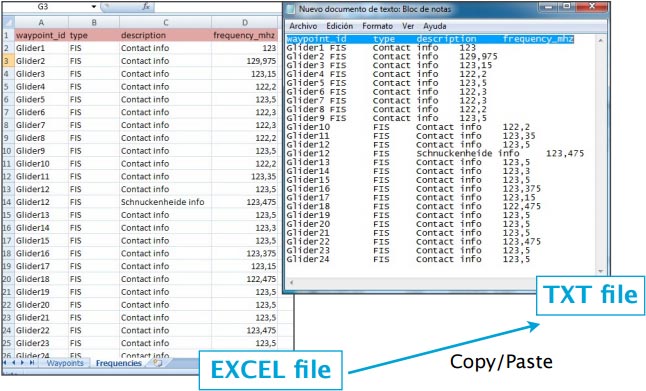
Estructura para frecuencias de contacto
To be valid, a frequencies file must start with a row listing the columns names separated by a tab character. The other lines are the actual frequencies values (1 line per frequency). Values can be empty but they must be separated by a tab character.
Columns names and definition are:
- waypoint_id (text, must match a waypoint waypoint_id to be associated with it)
- type (text, short name of the frequency)
- description (text, long name of the frequency)
- frequency_mhz (number with decimal, the actual frequency).
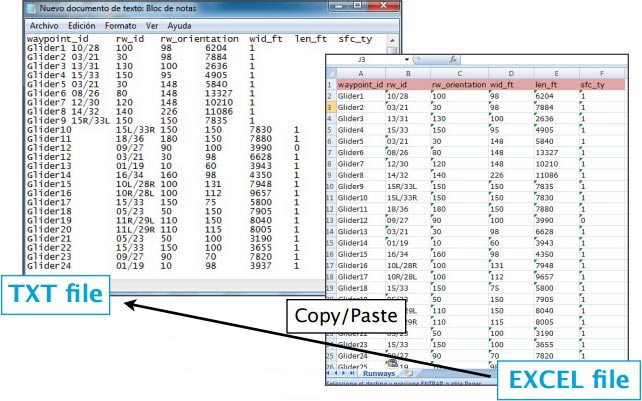
File structure for runways
To be valid, a runways file must start with a row listing the columns names separated by a tab character. The other lines are the actual runways values (1 line per runway). Values can be empty but they must be separated by a tab character.
Columns names and definition are:
- waypoint_id (text, must match a waypoint waypoint_id to be associated with it)
- rw_id (text, name of the runway)
- rw_orientation (number 1-360)
- wid_ft (number, width in feet)
- len_ft (number, length in feet)
- sfc_ty (number, unknown=0, Asphalt=1, Concrete=2, Grass=3, Gravel=4, Dirt=5, Sand=6, Snow=7, Ice=8, Water=9)
Note: remember that all the files described in this chapter will be imported into Air Navigation Pro through the embedded WebServer.
Back to index