(Created page with "Wegpunkte Format") |
(Created page with "<br /> ---- Um eine Liste von Wegpunkten über den '''Webserver''' zu importieren, müssen die Wegpunkte als Textdatei in UTF-8 Format gespeichert sein.") |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | + | Um eine Liste von Wegpunkten über den '''Webserver''' zu importieren, müssen die Wegpunkte als Textdatei in UTF-8 Format gespeichert sein. | |
You can use your favorite spreadsheet application or convert waypoints from another database to match the structure described below. | You can use your favorite spreadsheet application or convert waypoints from another database to match the structure described below. | ||
Revision as of 20:16, 15 June 2016
Um eine Liste von Wegpunkten über den Webserver zu importieren, müssen die Wegpunkte als Textdatei in UTF-8 Format gespeichert sein.
You can use your favorite spreadsheet application or convert waypoints from another database to match the structure described below.
We strongly recommend that you create a custom waypoint on the iPhone/iPod first and download it from the website to get the correct file structure, then you don’t have to type the columns names manually (which could result in typos and/or bad structure that would not be recognized as a valid file on importation).
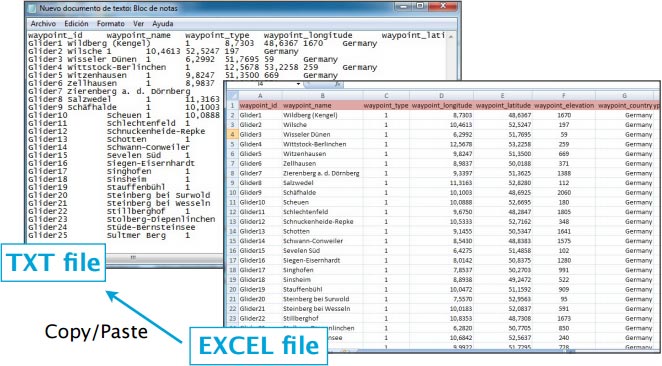
File structure for waypoints
To be valid, a waypoint file must start with a row listing the columns names separated by a tab character (TAB key). The other lines are the actual waypoints values (one line per waypoint). Values can be empty but they must be separated by a tab character.
The best would be to work on MS EXCEL and when having finished, then copy the columns and paste them into a TXT file with a program like «Notepad»:
Columns names and definition are:
- waypoint_id (text, usually less than 6 characters, required value)
- waypoint_name (text, longer description of the waypoint)
- waypoint_type (number: 1=Airport, 2=fix, 3=waypoint, 4=Helipad, 5=seaplane base, 8=IFR waypoint, 10=DME, 11=NDB, 12=VOR, 13=NDB/DME, 14=VOR/DME, 15=TACAN, 16=VORTAC)
- waypoint_longitude (number with decimal)
- waypoint_latitude (number with decimal)
- waypoint_elevation (number, elevation in feet)
- waypoint_country (text)
- waypoint_state (text, example California)
- waypoint_channel (text)
- waypoint_frequency (number, for navaids only)
- main_runway_orientation (number 1 to 360)
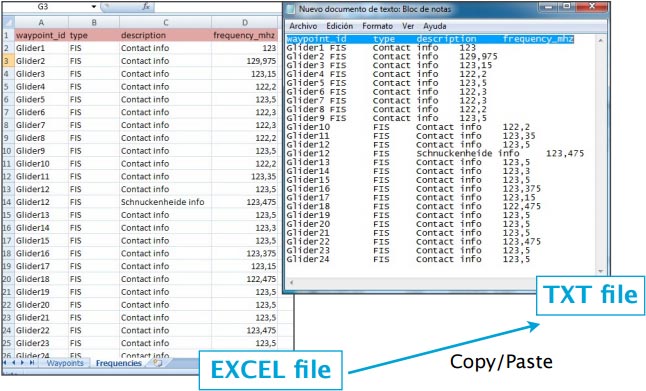
File structure for frequencies
To be valid, a frequencies file must start with a row listing the columns names separated by a tab character. The other lines are the actual frequencies values (1 line per frequency). Values can be empty but they must be separated by a tab character.
Columns names and definition are:
- waypoint_id (text, must match a waypoint waypoint_id to be associated with it)
- type (text, short name of the frequency)
- description (text, long name of the frequency)
- frequency_mhz (number with decimal, the actual frequency).
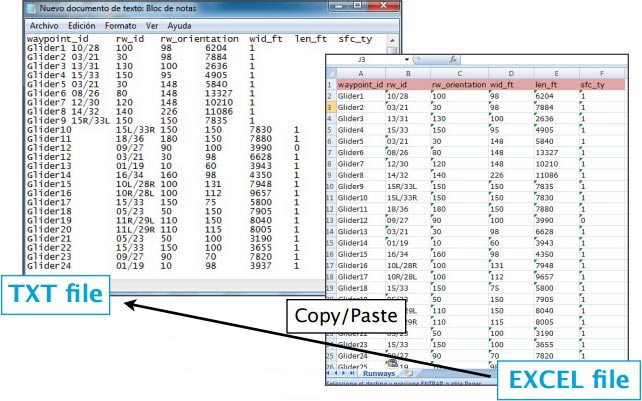
File structure for runways
To be valid, a runways file must start with a row listing the columns names separated by a tab character. The other lines are the actual runways values (1 line per runway). Values can be empty but they must be separated by a tab character.
Columns names and definition are:
- waypoint_id (text, must match a waypoint waypoint_id to be associated with it)
- rw_id (text, name of the runway)
- rw_orientation (number 1-360)
- wid_ft (number, width in feet)
- len_ft (number, length in feet)
- sfc_ty (number, unknown=0, Asphalt=1, Concrete=2, Grass=3, Gravel=4, Dirt=5, Sand=6, Snow=7, Ice=8, Water=9)
Back to previous page.